“`html
Logical Fallacy
Definition of Logical Fallacy
A logical fallacy is a flaw in reasoning that often undermines the logical validity of an argument. Because they can appear persuasive, these errors in reasoning are frequently used to manipulate opinions by appealing to emotions rather than logic. Understanding logical fallacies is crucial for constructing sound and robust arguments both in everyday discussions and professional settings.
Importance of Understanding Logical Fallacies
Grasping the nuances of logical fallacies is necessary because it empowers individuals to recognize and counter flawed arguments. With knowledge of common fallacies, one can enhance their analytical skills and promote more meaningful, productive conversations. Additionally, by mastering the identification of these errors, one can contribute to reducing misinformation, which is increasingly prevalent in the digital age. Despite the complexity of some fallacies, being aware of their presence ensures you engage in more rational discussions. Furthermore, this understanding encourages critical thinking, fostering a culture of open-mindedness and reasoned debate.
“`
Common Types of Logical Fallacies
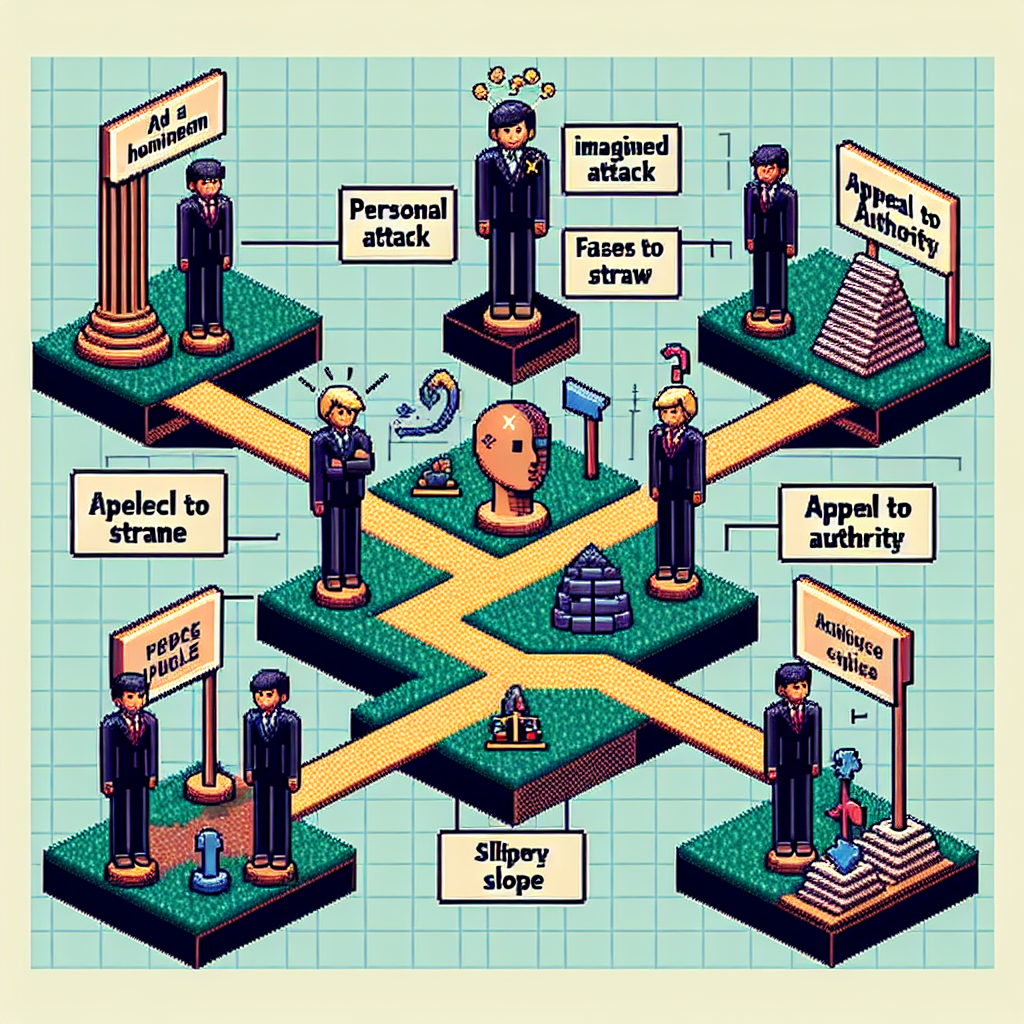
Ad Hominem
An ad hominem logical fallacy occurs when someone attacks the person making the argument instead of addressing the actual argument itself. This can distract from the main issue and divert attention away from valid points, creating an unfair bias in evaluations.
Straw Man
The straw man logical fallacy involves misrepresenting an opponent’s argument to make it easier to refute. This often leads to oversimplification and can prevent productive dialogue, because the original argument is not accurately addressed.
Appeal to Authority
An appeal to authority occurs when someone claims something must be true simply because an expert or authority states it. While experts are valuable, this fallacy disregards the necessity of evidence or logical reasoning behind the claim.
False Dilemma
A false dilemma presents a situation as having only two opposing options, ignoring the possibility of any alternatives. This can lead to limited thinking and decision-making, even though multiple solutions may exist.
Slippery Slope
The slippery slope logical fallacy suggests that one small step will inevitably lead to a chain of related events, often with negative outcomes. This fallacy overlooks the complexity of situations and the many variables that can influence them, leading to fear-based decisions.
How Logical Fallacies Are Used
In Debates and Arguments
During debates, individuals may employ a logical fallacy to undermine their opponent’s argument instead of addressing the core issue. Additionally, this tactic can appear convincing because it diverts attention from weak points. However, when audiences are aware of these techniques, they become better equipped to evaluate the validity of each argument.
In Marketing and Advertising
Marketing campaigns frequently utilize logical tactics to influence consumer decisions. A logical fallacy may be used to obscure facts or create misleading perceptions about a product’s effectiveness. Despite being effective in driving short-term results, this approach can damage brand credibility in the long run. Brands should focus on transparency to build trust with consumers.
In Social Media and Viral Content
Logical fallacies are often prevalent in viral content due to their catchy and provocative nature. They spread quickly across social media platforms because they simplify complex issues. Yet, the simplicity may lead to misinformation. Platforms can implement fact-checking processes to help users identify deceptive content, encouraging critical thinking.
Identifying a Logical Fallacy
Key Indicators of Unwarranted Precision
One salient marker of a Logical Fallacy is unwarranted precision. This occurs when details are presented with seemingly precise statistics or information, lending an undeserved air of accuracy. Such tactics can often mislead audiences. As a result, it is crucial to scrutinize the origin and validity of every statistic or claim, ensuring they are backed by credible sources.
Common Mistakes When Identifying Fallacies
Despite efforts to accurately identify logical fallacies, common mistakes are made. People may overemphasize trivial errors while overlooking significant oversights. This can lead to misinterpretations. Before jumping to conclusions, it’s important to focus on the context and intent of arguments to avoid missing the bigger picture.
Tools and Resources for Detection
During the evaluation process, several tools and resources are available to aid in detecting fallacies. Fact-checking websites and forums focusing on logical reasoning can provide valuable insights. Additionally, engaging with communities dedicated to debate and logic can refine our abilities to spot fallacies. These resources contribute significantly to enhancing one’s analytical skills, ultimately leading to more precise identification of logical inconsistencies.
“`xml
Logical Fallacy and Their Impact on SEO
Influence on Content Credibility
The presence of a logical fallacy in your content can significantly impact its credibility. A single misstep in reasoning can cause readers to question the validity of the entire piece. Additionally, search engines prioritize content that demonstrates reliability and accuracy. Therefore, avoiding fallacies is crucial for maintaining a strong online presence.
Effects on Audience Trust
When audiences recognize a logical fallacy, they often lose trust in the source. This distrust is not confined to the initial content but can extend to other materials produced by the same author or organization. Despite efforts to rebuild this trust, the impact of a lack of credibility can linger. Building ongoing trust requires consistently high-quality, fallacy-free content.
Misleading Analytics and Metrics
Content riddled with logical fallacies can achieve misleading metrics such as click-through rates or engagement. However, these figures might not reflect genuine interest or trust from the audience. During the process of analyzing SEO strategies, it is vital to discern between superficial metrics and those indicating authentic audience connection. This ensures that both content strategies and SEO outcomes align with company goals.
“`
“`HTML
Best Practices to Avoid Using Logical Fallacies in Content
Fact-Checking and Verification
To avoid using a Logical Fallacy in your content, it’s crucial to engage in thorough fact-checking and verification. Ensuring the accuracy of your data builds a solid foundation for credibility. Additionally, cross-referencing sources can reveal discrepancies and enhance the quality of information, preventing errors from infiltrating your content.
Clear and Precise Language
Communicating with clear and precise language is another effective strategy. By expressing your ideas unequivocally, you minimize the risk of misinterpretation. This approach reduces the likelihood of inadvertently supporting a Logical Fallacy. Therefore, it’s essential to use language that prevents confusion and supports accurate understanding.
Encouraging Critical Thinking in Audiences
Encouraging critical thinking among your audience fosters an environment where logical analysis and reasoning prevail. During content creation, pose questions that invite reflection and engagement. This not only enhances your readers’ analytical skills but also discourages the passive acceptance of potentially flawed arguments.
“`
Benefits of Avoiding Logical Fallacies in Content
Enhancing Content Reliability
Consider the case of a digital publication known for its rigorous fact-checking processes and its commitment to clear and precise language. This publication noticed a significant increase in its readership over time because readers trusted the accuracy of the information provided. By systematically avoiding any Logical Fallacy, they ensured that the content was not just engaging but also reliable. This approach led to fewer corrections and retractions, boosting their reputation as a dependable source of news and information.
Building Authority and Trustworthiness
As the publication focused on maintaining high content standards, it naturally began to build a reputation for authority and trustworthiness in the industry. Regular readers, as well as new audience members, began to see it as a leader in delivering factual content. Additionally, the disciplined approach helped in establishing strong relationships with experts who were more willing to contribute or be cited, further reinforcing their market position.
Improving Engagement and Conversion Rates
During this transformation, the publication also observed enhanced engagement and conversion rates. Readers were more likely to share articles, participate in discussions, and subscribe to premium content plans. Although some initial investments were made in training editors and writers to identify and avoid Logical Fallacies, the long-term benefits outweighed these costs. By encouraging critical thinking among audiences, the publication successfully fostered an interactive community, resulting in substantial growth in both audience size and loyalty.